Courses that do not follow the traditional start and end dates of the standard Fall and Spring terms are classified as Non-Standard terms. This category includes all summer sessions as well as many online or hybrid graduate programs.
Terminology
Rate of Pursuit (Chapter 33 Post-9/11 GI Bill ONLY)
Your rate of pursuit is based on the number of credits you are enrolled in during a given term, and is expressed as a percentage of full-time status, rounded to the nearest 10%.
An undergraduate student in a normal semester is considered full-time (100% rate of pursuit) at 12 or more credits.
A graduate student in a normal semester is considered full-time (100% rate of pursuit) at 9 or more credits unless the student’s full-time status is defined differently by the University Registrar. Examples of this include students holding full-time assistanceships or students working on dissertation credits who have been approved by their departments to reduce their full-time credit requirements.
Your rate of pursuit is used to calculate monthly housing allowance payments and the amount of time deducted from your benefit.
Your rate of pursuit does not affect tuition and fee payments to the school. Your tuition and fees will be paid based on your eligibility percentage.
Rate of pursuit calculations are different for non-standard terms.
Eligibility Percentage (Chapter 33 Post-9/11 GI Bill ONLY)
This your eligibility percentage of the Post-9/11 GI Bill, as determined by the VA, based on the length and circumstances of your military service or the military service of the person who transferred benefits to you.
A student with 100% eligibility under the Post-9/11 GI Bill will have 100% of eligible tuition and course fees covered and receive 100% of the monthly housing allowance (if applicable) and book stipend (if applicable).
A student with a lower eligibility percentage will have a proportionately smaller percentage of tuition and course fees covered, and a receive a proportionately smaller percentage of the housing allowance, and book stipend.
You can find your eligibility percentage on your certificate of eligibility, on your VA eBenefits account, or by contacting the VA directly.
Eligibility percentage is not related to the number of months of Chapter 33 you have remaining, the number of months of Chapter 33 you had transferred to you, your VA disability rating, or the VA disability rating of the person who transferred benefits to you.
The Chapter 33 examples in these instructions assume 100% Post-9/11 GI Bill eligibility.
Training Time (NON-Chapter 33 ONLY)
Your training time is expressed as a fraction of full-time status. Your training time may be full-time, ¾ time, ½ time, less than ½ but greater than ¼ time, or ¼ time.
Full Time Modifier
This is the number of credits in which a graduate student must be enrolled to be considered full-time in a non-standard term
Credit Hour Equivalents/Credit Hour Equivalency
This is a calculation the VA makes during non-standard terms to compare the number of credits a student is taking to what the equivalent hours would be in a standard semester.
Term
A term is a distinct period of time in which a student is in class. Examples of distinct, individual terms include summer sessions, a fall or spring standard semester, an eight-week module in an MBA program, or a two-week study abroad.
The VA treats each of these as distinct, individual entities when determining how they will charge your benefits, even if they have overlapping dates.
Standard Semester
A full semester, or standard semester runs 15 to 19 weeks. For the purpose of using VA benefits at George Mason, only the full-length Fall and Spring terms (including Mason-Korea terms) are considered standard semesters.
Non-Standard Term
A non-standard term at Mason is any period you are in class that is not a full standard semester in length. It can be outside of the standard semester dates, fall within those dates, or overlap those dates. Shorter non-standard termsgenerally require fewer credits to reach full-time status.
Modules
Some programs at George Mason are offered in modules. These are typically 8-weeks in length, and there are usually two modules within in a standard semester. Each module is treated as a separate, distinct term by the VA.
48-Month Rule
The VA limits veterans and servicemembers to a total of 48 months of benefits if they have more than one GI Bill benefit based on their own service. Veterans and servicemembers who use the full 36 months of Chapter 30 Montgomery GI Bill – Active Duty benefits may qualify for an additional 12 months of Chapter 33 Post-9/11 GI Bill.
This 48-month cap may be extended to the end of the term in which a student exhausts benefits under the Carr v. Wilkie ruling if the student reaches his or her 48-month cap in the middle of a term on or after June 11, 2019. This determination is made by the VA, and does not apply to students using benefits transferred to them.
Chapter 33 Non-Standard Term - Undergraduate
When George Mason reports your enrollment(s) to the VA, we provide the number of credits in which you are enrolled and the term(s) those classes fall under. Rate of pursuit must be greater than 50% in order to receive a monthly housing allowance.
In a non-standard term, the VA determines your credit hour equivalent using the following formula:
Credits x 18 / Weeks
The VA calculates the number of weeks in a term by taking the number of days in a term and dividing by 7. They will then round to the nearest week (for example, 8 weeks and 3 days is rounded to 8 weeks, while four weeks and 4 days is rounded to 5 weeks).
The VA multiplies the number of credits you are taking in the term by 18. They divide this number by the number of weeks of the term.
The VA then compares this credit hour equivalent to the above table to determine your rate of pursuit.
Example:
You are in a 3-credit undergraduate class during the Summer A Session term. This term is 5 weeks in length. (3 credits x 18) ÷ 5 weeks = 10.8 (rounded to 11).
The VA determines that 3 credits in five weeks is the equivalent of 11 credits in a normal undergraduate semester. Looking at the table above, we see that 11 credits in a normal semester is a 90% rate of pursuit.
For these five weeks, you will receive applicable stipends at a 90% rate of pursuit, and the VA will deduct 90% of five weeks from your remaining entitlement.
If your classes are in overlapping terms, the VA will use whichever rate of pursuit calculation is highest during the overlap period. While this benefits you from a housing stipend perspective, you should be aware that your benefit is also being reduced at the higher rate.
Example:
You are a Chapter 33 undergraduate student in a total of 12 credits: three 3 credit classes that run from 1/24 to 5/10 and one 3 credit class from 3/15 to 4/25. We report this as two separate enrollments: 9 credits under the Spring standard semester and 3 credits as a non-standard term.
In this scenario, you would receive multiple rate of pursuit calculations from the VA.
Beginning on 1/24, you are in 9 standard semester credits. You would need to be in 12 credits to have a 100% rate of pursuit. Your benefits during this period are charged at an 80% rate of pursuit, and you receive 80% of the monthly housing allowance (if applicable). This rate of pursuit changes when the non-standard term starts.
In the middle of these standard semester classes, your non-standard term class begins.
Beginning on 3/15, you are now in a total of 12 credits, and have a 100% rate of pursuit. Your benefits during this period are charged at the 100% rate of pursuit, and you receive 100% of the monthly housing allowance (if applicable). This rate of pursuit changes when your non-standard term ends.
When the non-standard term class ends on 4/25, you are again in 9 credits, and you return to an 80% rate of pursuit. Your benefits are charged at an 80% rate of pursuit, and you receive 80% of the monthly housing allowance (if applicable).
Chapter 33 Non-Standard Term - Graduate
When George Mason reports your enrollments to the VA, we provide the number of credits in which you are enrolled and the terms those classes fall under. We also tell the VA how many credit hours are considered full-time for the term in which you are enrolled.
In a standard semester, full-time status usually requires a student to be enrolled in nine credits. Some students may be in programs that only require six or fewer credits to be considered full-time. This may include students are enrolled in dissertation credits, students holding full-time assistantships, students working on theses, and others. Check with your advisor if you are unsure of your full-time requirements.
In a non-standard term, we will report a full-time modifier, which is based on the length of your term.
Calculate the number of weeks in a term by taking the number of days in a term and dividing by 7. Round to the nearest week (for example, 8 weeks and 3 days is rounded to 8 weeks, while four weeks and 4 days is rounded to 5 weeks).
Consult the appropriate chart below to determine your full-time modifier for the term in question.
To determine your rate of pursuit, take the number of credits in which you are enrolled in a given term and divide by the full-time modifier. Round to the nearest tenth. For example, 0.74 is rounded to 0.7, or a 70% rate of pursuit, while 0.75 is rounded to 0.8, or an 80% rate of pursuit. Your rate of pursuit must be greater than 50% in order to receive a monthly housing allowance.
Standard Graduate Full-Time Requirements:
|
Course Length in Weeks |
Full Time Modifier (9 credit students) |
|
1 |
1 |
|
2 |
1 |
|
3 |
1 |
|
4 |
2 |
|
5 |
2 |
|
6 |
3 |
|
7 |
3 |
|
8 |
4 |
|
9 |
4 |
|
10 |
5 |
|
11 |
5 |
|
12 |
6 |
|
13 |
6 |
|
14 |
7 |
|
15-19 |
9 |
Modified Graduate Full-Time Requirements (examples include enrolled in dissertation credits, students holding full-time assistantships, students working on thesis)
|
Course Length in Weeks |
Full Time Modifier (3 credit students) |
Full Time Modifier (6 credit students) |
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
2 |
1 |
1 |
|
3 |
1 |
1 |
|
4 |
1 |
1 |
|
5 |
1 |
1 |
|
6 |
1 |
2 |
|
7 |
1 |
2 |
|
8 |
1 |
2 |
|
9 |
1 |
3 |
|
10 |
1 |
3 |
|
11 |
1 |
3 |
|
12 |
2 |
4 |
|
13 |
2 |
4 |
|
14 |
2 |
4 |
|
15-19 |
3 |
6 |
Chapter 30, 35 or 1606 Non-Standard Term - Undergraduate
When George Mason reports your enrollments to the VA, we provide the number of credits in which you are enrolled and the terms those classes fall under.
The VA will use the training time table to determine your monthly stipend and the rate at which your benefit is charged. This will be at the full-time, ¾ time, ½ time, less than ½ but greater than ¼ time, or ¼ time rate.
Students who are on active duty or students who are less-than-half-time cannot receive payments that total more than the actual cost of tuition and course fees during a term. The VA may reduce your monthly payments so they do not exceed this amount.
We are required to report your actual course dates.
Chapters 30, 35, 1606 Undergraduate Training Time Table
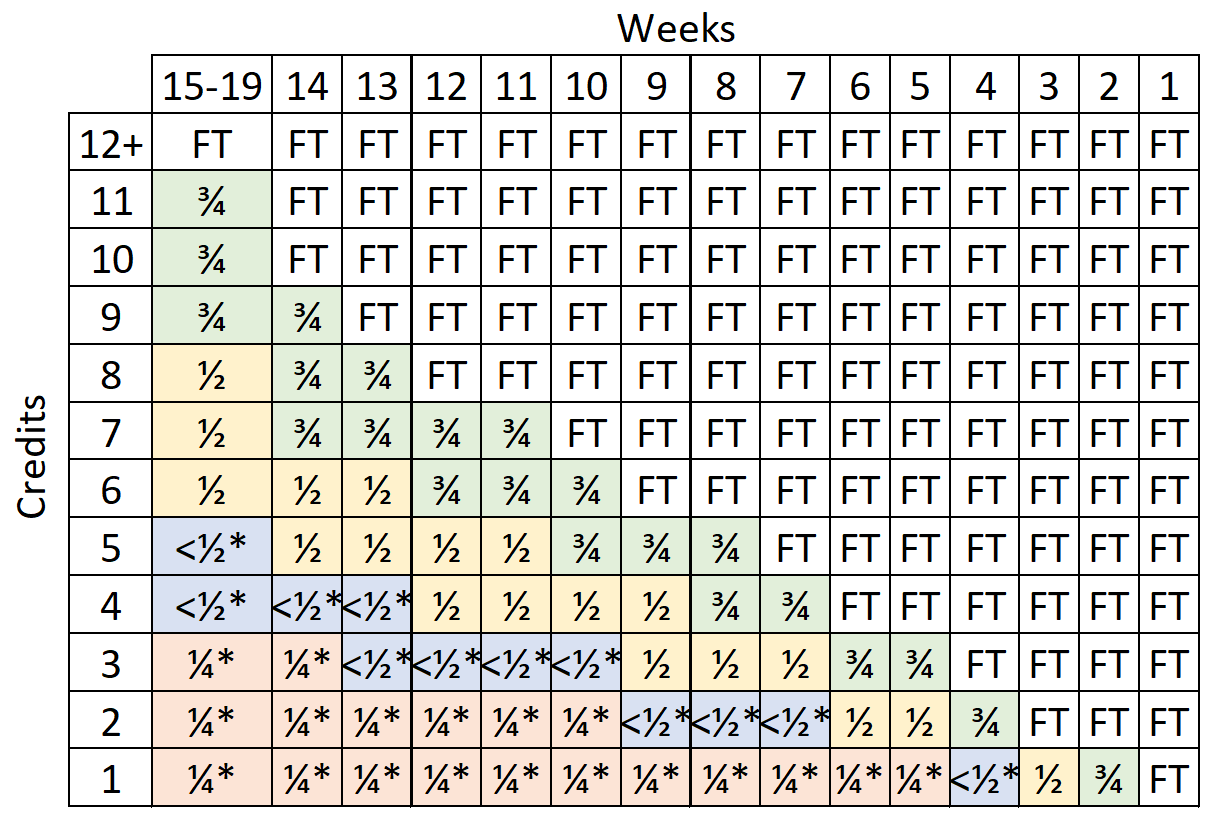
*Total payments cannot exceed the actual cost of your tuition and fees. If your classes are in overlapping terms, the VA will use whichever training time is highest during the overlap period. While this benefits you from a stipend perspective, you should be aware that your benefit is also being reduced at the higher rate.
Chapter 30, 35 or 1606 Non-Standard Term - Graduate
When George Mason reports your enrollments to the VA, we provide the number of credits in which you are enrolled and gthe terms thos classes fall under. We also report your training time.
The VA will use the training time reported by the school to determine your monthly stipend and the rate at which your benefit is charged. This will be at the full-time, ¾ time, ½ time, less than ½ but greater than ¼ time, or ¼ time rate.
Students who are on active duty or students who are less-than-half-time cannot receive payments that total more than the actual cost of tuition and course fees during a term. The VA may reduce your monthly payments so they do not exceed this amount.
We are required to report your actual course dates.
Graduate Full Semester Training Time Table
|
Credits |
Training Time |
|
9+ |
Full Time |
|
6-8 |
¾ |
|
4.5-5.5 |
½ |
|
4.4 or fewer |
<½ |
You may estimate your training time in non-standard terms by using the credit hour equivalent formula:
Credits x 18 / Weeks
-
Calculate the number of weeks in a term by taking the number of days in a term and dividing by 7. Round to the nearest week (for example, 8 weeks and 3 days is rounded to 8 weeks, while four weeks and 4 days is rounded to 5 weeks).
-
Multiply the number of credits by 18. Divide this number byb the number of weeks in the term.
-
Compare this credit hour equivalent to the above table to determine your training time.
Example: You are a Chapter 35 graduate student in one 8-week course for 3 credits from 1/11 to 3/7.
(3 credits x 18) ÷ 8 weeks = 6.75. Based on the table above, 3 credits in eight weeks is the equivalent of 6.75 credits in a normal semester. Your benefits during this period are charged at ¾ training time, and you receive the ¾ rate Chapter 35 stipend.
If your classes are in overlapping terms, the VA will use whichever training time is highest during the overlap period. While this benefits you from a stipend perspective, you should be aware that your benefit is also being reduced at the higher rate.
Non-Standard Terms and Benefit Exhaustion
If you are using Chapter 33 benefits and you exhaust benefits in the middle of a term, the VA will pay through the end of the term in which you are enrolled, provided you have not reached your delimiting date or reached the VA cap of 48 months of total benefits.
If you are close to exhausting Chapter 33 benefits, it is important to check the start and end dates of each of your courses. The VA will not pay for terms that begin after the exhaustion of benefits.
Example:
You are a veteran student using your own Chapter 33 benefit in a module-based program. One module begins on 1/11 and ends on 3/7. Your other module begins on 3/15 and ends on 5/10. The VA notifies you that you will exhaust your 36 months of Chapter 33 benefits on 2/12.
Because you are a veteran using your own benefit, the VA will pay tuition, fees, and the housing stipend (if applicable) for the entire term that began on 1/11 and ends on 3/7. The VA will not pay for the term that begins on 3/15, because it falls outside of your exhaustion date.
Please note that this information is for informational purposes only. It does not constitute a formal VA determination of how your individual benefits will be processed, paid, charged, or administered. All examples are illustrative only.
Please contact the office to discuss the benefits process for these situations. Be sure to mention if you are in a semester or modular based program. If we don't know, the general information shared is based on standard terms.
